| SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro | SOFTWARE MANUAL |
| 2. Designating image files for processing | ||||||||
To perform RAW data processing on SILKYPIX ®, first designate an image file (RAW / JPEG / TEFF / DNG) for processing.
There are two methods for designating image files: in file units or in folder units.
You can designate files or folders through dialogs, by selecting from history up to that point and by drag and drop methods.
There is also a way to add image files for processing when other image files are already designated for processing.
If image files and folders are designated for new processing, image files that had been set for processing to that point will automatically be closed.
If you designate image files and folders through the method for adding image files for processing, the newly designated image files will be added to the image files for processing to that point.
2.1. Opening File
2.1.1. Selecting from dialogs
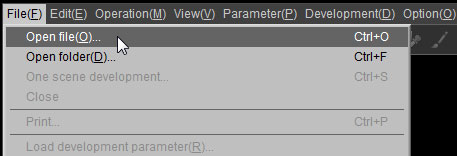 This is a method for designating image files for processing in file units. You can designate multiple files. You can also add files.
This is a method for designating image files for processing in file units. You can designate multiple files. You can also add files.
Select [File (F)] [Open file (O)] from the menu or click on the icon in the tool bar to display the [Open file] dialog.
icon in the tool bar to display the [Open file] dialog.
You can designate one or more image files for processing from the [Open file] dialog.
When selecting multiple image files for processing, do so while holding down either the [SHIFT] key or [CTRL] key.
After selecting multiple files for processing, next designate whether they are for new processing or for adding to processing.
When the [CTRL] key is pushed, the "Open (O)" button changes into an "Add and open (O)" button. If adding, please click on the "Add and open (O)" button in this status.
If you click [Open(O)] button without clicking [CTRL] key, the RAW data files is closed automatically which have been already loaded for processing.
And the RAW data files selected in this time is loaded instead of them.
2.1.2. Selecting from file history
 This is a method for designating image files for processing in file units. You can designate multiple files. You can also add files.
This is a method for designating image files for processing in file units. You can designate multiple files. You can also add files.Select [File (F)] [Open file (O)] from the menu or click on the
 icon in the tool bar to display the [Open file] dialog.
icon in the tool bar to display the [Open file] dialog.You can designate one or more image files for processing from the [Open file] dialog.
When selecting multiple image files for processing, do so while holding down either the [SHIFT] key or [CTRL] key.
After selecting multiple files for processing, next designate whether they are for new processing or for adding to processing.
When the [CTRL] key is pushed, the "Open (O)" button changes into an "Add and open (O)" button. If adding, please click on the "Add and open (O)" button in this status.
If you click [Open(O)] button without clicking [CTRL] key, the RAW data files is closed automatically which have been already loaded for processing.
And the RAW data files selected in this time is loaded instead of them.
You can select image files for processing in file units from file history to that point.
You can designate only one file when designating files by this method. You cannot designate multiple files nor add files.
There are two ways to make selections from file history. The first is to open [File (F)] from the menu and display a list of file history at the bottom of the menu.
The other method is to click on the mark located to the side of the
mark located to the side of the  (file icon) on the tool bar.
(file icon) on the tool bar.
Use one of these methods to select one file from the list.
2.1.3. Designating by drag and drop You can designate only one file when designating files by this method. You cannot designate multiple files nor add files.
There are two ways to make selections from file history. The first is to open [File (F)] from the menu and display a list of file history at the bottom of the menu.
The other method is to click on the
 mark located to the side of the
mark located to the side of the  (file icon) on the tool bar.
(file icon) on the tool bar.Use one of these methods to select one file from the list.
This is a method for dropping image files for processing into SILKYPIX ® from a tool that files can be dragged from, such as Explorer or Finder.
If files that are not for processing are included, they cannot be dropped. Multiple files can be designated. Files can also be added.
If you start dragging with a left drag, files dropped into SILKYPIX ® will be available for new processing. Image files for processing up to that point will be automatically closed.
If you start dragging with a right drag, when you drop them into SILKYPIX ® a menu will appear for selecting the processing method. You can select new processing, adding or cancel processing for the dropped files.
However, if there are no image files for processing up to that point, the menu will not appear and they will be processed as new processing.
If files that are not for processing are included, they cannot be dropped. Multiple files can be designated. Files can also be added.
If you start dragging with a left drag, files dropped into SILKYPIX ® will be available for new processing. Image files for processing up to that point will be automatically closed.
If you start dragging with a right drag, when you drop them into SILKYPIX ® a menu will appear for selecting the processing method. You can select new processing, adding or cancel processing for the dropped files.
However, if there are no image files for processing up to that point, the menu will not appear and they will be processed as new processing.
2.2. Opening Folder
2.2.1. Selecting from dialogs
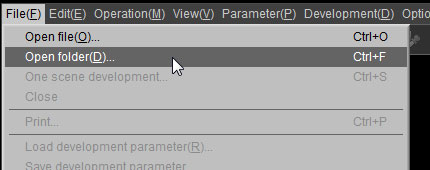 Open Folder function allows you to select and load the RAW data files from the specified folder. All image files for processing in the designated folder will be processed. This will be designated as new processing, and image files for processing up to that point will be automatically closed.
Open Folder function allows you to select and load the RAW data files from the specified folder. All image files for processing in the designated folder will be processed. This will be designated as new processing, and image files for processing up to that point will be automatically closed.
Select [File (F)] [Open folder (D)] from the menu or click on the icon in the tool bar to display the [Select folder for processing] dialog.
icon in the tool bar to display the [Select folder for processing] dialog.
Folders with image files for editing are designated from this dialog.
2.2.1.1. Load from Sub-folder
2.2.2. Selecting from folder history
 Open Folder function allows you to select and load the RAW data files from the specified folder. All image files for processing in the designated folder will be processed. This will be designated as new processing, and image files for processing up to that point will be automatically closed.
Open Folder function allows you to select and load the RAW data files from the specified folder. All image files for processing in the designated folder will be processed. This will be designated as new processing, and image files for processing up to that point will be automatically closed.Select [File (F)] [Open folder (D)] from the menu or click on the
 icon in the tool bar to display the [Select folder for processing] dialog.
icon in the tool bar to display the [Select folder for processing] dialog.Folders with image files for editing are designated from this dialog.
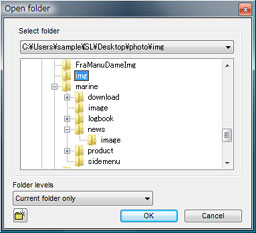 Select folder dialog of Windows | 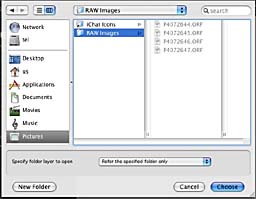 Select folder dialog of Macintosh |
2.2.1.1. Load from Sub-folder
There is an option to load RAW data from sub folders according to the method of "Folder levels" on the "Select folder" dialog.
You can load the RAW data from the sub folder of the selected folder with this option.
By using this option, you can simultaneously designate image files dispersed and stored in multiple folders located hierarchically.
You can load the RAW data from the sub folder of the selected folder with this option.
By using this option, you can simultaneously designate image files dispersed and stored in multiple folders located hierarchically.
You can select image files for processing in folder units from folder history to that point.
You can designate only one folder when designating files by this method. You cannot add image files for processing. You can designate sub-folders.
There are two ways to make selections from folder history. The first is to open [File (F)] from the menu and display a list of folder history at the bottom of the menu.
The other method is to click on the mark located to the side of the
mark located to the side of the  (folder icon) on the tool bar.
(folder icon) on the tool bar.
Use one of these methods to select one file from the list.
Furthermore, if you move the mouse cursor to the right edge of the menu, a submenu will appear. You can designate subfolders from this submenu.
2.2.3. Assign Using Drag & Drop You can designate only one folder when designating files by this method. You cannot add image files for processing. You can designate sub-folders.
There are two ways to make selections from folder history. The first is to open [File (F)] from the menu and display a list of folder history at the bottom of the menu.
The other method is to click on the
 mark located to the side of the
mark located to the side of the  (folder icon) on the tool bar.
(folder icon) on the tool bar.Use one of these methods to select one file from the list.
Furthermore, if you move the mouse cursor to the right edge of the menu, a submenu will appear. You can designate subfolders from this submenu.
This is a method for dropping a folder from tools that allow you to drag folders, such as Explorer and Finder, to SILKYPIX ®. Only one folder can be dropped. If multiple folders are selected, they cannot be dropped. Furthermore, you cannot designate subfolders.
An error will be shown if a folder that does not include an image file for processing is dropped. Drop folders that include an image file for processing.
If a drag begins as a left drag, the folder dropped to SILKYPIX ® will be subject to new processing. Image files that had been subject to processing to that point will be automatically closed.
If a drag begins as a right drag, a menu will appear for selecting processing methods for that which was dropped to SILKYPIX ®. You can choose new processing, adding or cancel processing of the dropped folder.
However, if there are no image files that had been subject to new processing to that point, the menu will not appear and it will be treated as being subject to new processing.
An error will be shown if a folder that does not include an image file for processing is dropped. Drop folders that include an image file for processing.
If a drag begins as a left drag, the folder dropped to SILKYPIX ® will be subject to new processing. Image files that had been subject to processing to that point will be automatically closed.
If a drag begins as a right drag, a menu will appear for selecting processing methods for that which was dropped to SILKYPIX ®. You can choose new processing, adding or cancel processing of the dropped folder.
However, if there are no image files that had been subject to new processing to that point, the menu will not appear and it will be treated as being subject to new processing.
2.3. When RAW data does not open as expected
If RAW data does not open as expected, it may be that the RAW data is corrupt or that the RAW data is not compatible with this software.
Refer to the compatibility camera list and check that the RAW data can be used with this software.
If RAW data from a incompatible camera is read, a warning such as, "A camera not supported has been detected," may be shown. Even so, operations such as developing may be performed, but colors from cameras not supported may be strange or other trouble may occur, so please do not use them.
In addition to RAW data (including DNG), JPEG image and TIFF image files can be processed by this software. Please note that there are some types of files that are not supported, even if they are DNG, JPEG images or TIFF images.
Initial settings will open RAW data, JPEG images and TIFF images, but there is also a mode that makes only RAW data subject to processing. Please see "9.3.1.6. Processing only RAW Data" for details.
Refer to the compatibility camera list and check that the RAW data can be used with this software.
If RAW data from a incompatible camera is read, a warning such as, "A camera not supported has been detected," may be shown. Even so, operations such as developing may be performed, but colors from cameras not supported may be strange or other trouble may occur, so please do not use them.
In addition to RAW data (including DNG), JPEG image and TIFF image files can be processed by this software. Please note that there are some types of files that are not supported, even if they are DNG, JPEG images or TIFF images.
Initial settings will open RAW data, JPEG images and TIFF images, but there is also a mode that makes only RAW data subject to processing. Please see "9.3.1.6. Processing only RAW Data" for details.
2.4. How to Handle JPEG/TIFF Image
SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro has the feature of developing JPEG/TIFF image like the RAW data, which is called "SILKYPIX® RAW Bridge".
It may seem strange to use the word "development" for JPEG/TIFF image, however, it is extremely convenient to process JPEG/TIFF images RAW files by using the same parameters.
There is a difference between SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro and a photo retouching software: SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro does something like an "inverse transformation" from a JPEG/TIFF image to a virtual RAW image and then treats them same as RAW data internally.
Therefore, SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro does the color processing which is more correct than photo retouching software can be done.
As a result, you can use most functions with a sense similar to that of handling RAW data with extensions such as ".JPG" and ".TIF."
JPEG/TIFF Processing Mode is enabled in the default setting, please refer to '4.8.4 JPEG/TIFF Processing Mode' for the details.
SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro processes tone interpolation and wide reproduction color mapping for JPEG/TIFF images, but JPEG/TIFF images have too little information compared to genuine RAW.
The substantial adjustment for JPEG/TIFF images causes the failure of the image.
2.4.1. Color temperature of JPEG / TIFF images
It may seem strange to use the word "development" for JPEG/TIFF image, however, it is extremely convenient to process JPEG/TIFF images RAW files by using the same parameters.
There is a difference between SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro and a photo retouching software: SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro does something like an "inverse transformation" from a JPEG/TIFF image to a virtual RAW image and then treats them same as RAW data internally.
Therefore, SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro does the color processing which is more correct than photo retouching software can be done.
As a result, you can use most functions with a sense similar to that of handling RAW data with extensions such as ".JPG" and ".TIF."
JPEG/TIFF Processing Mode is enabled in the default setting, please refer to '4.8.4 JPEG/TIFF Processing Mode' for the details.
SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro processes tone interpolation and wide reproduction color mapping for JPEG/TIFF images, but JPEG/TIFF images have too little information compared to genuine RAW.
The substantial adjustment for JPEG/TIFF images causes the failure of the image.
2.4.1. Color temperature of JPEG / TIFF images
For the "RAW data", you can use the absolute "color temperature" to adjust white balance.
For example to the scene to have taken the photograph under the 3000K bulb, you can get the approximately right white balance if you set "color temperature" on 3000K.
However, with JPEG / TIFF images, this is after white balance processing has been done on the camera, so unfortunately the color temperature at the time the photograph was taken cannot be set to standard reference.
Supposing there are JPEG / TIFF images that have had perfect white balance adjustments, they cannot be distinguished, no matter what source of light these photographs were taken under.
For actual photographed JPEG / TIFF images, the influence of the light source at the time it was taken will remain, but in either case the color temperature at the time it was taken cannot be ascertained, so the default white balance values are fixed at color temperature = 6500K, color deviation = 3. This color temperature is the white point value for sRGB and Adobe RGB.
Whatever light source the JPEG / TIFF images were taken under, they will be processed under the assumption of having been taken under a light source of 6500K.
Please understand that if you make adjustments to white balance on JPEG / TIFF images, they will be adjustments relative to this color temperature = 6500K, color deviation = 3.
As this is not the actual color temperature of the light source when the photograph was taken, you may feel there is a contradiction, but what is strange with this processing format is the displayed color temperature may be inaccurate. There are no limitations to adjusting the white balance.
Relative adjustments are adjustments to the three parameters, color temperature, color deviation and shading adjustments that diverge from the default values color temperature = 6500K, color deviation = 3. The numerical value of color temperature itself is an assumed value and has no meaning, so this method cannot be used to designate white balance with absolute values of color temperature.
Usage is the same as that of "Auto" white balance, gray balance tools and skin color designation tools on RAW data.
2.4.2. Sharpness/Noise Reduction for JPEG/TIFF Processing For example to the scene to have taken the photograph under the 3000K bulb, you can get the approximately right white balance if you set "color temperature" on 3000K.
However, with JPEG / TIFF images, this is after white balance processing has been done on the camera, so unfortunately the color temperature at the time the photograph was taken cannot be set to standard reference.
Supposing there are JPEG / TIFF images that have had perfect white balance adjustments, they cannot be distinguished, no matter what source of light these photographs were taken under.
For actual photographed JPEG / TIFF images, the influence of the light source at the time it was taken will remain, but in either case the color temperature at the time it was taken cannot be ascertained, so the default white balance values are fixed at color temperature = 6500K, color deviation = 3. This color temperature is the white point value for sRGB and Adobe RGB.
Whatever light source the JPEG / TIFF images were taken under, they will be processed under the assumption of having been taken under a light source of 6500K.
Please understand that if you make adjustments to white balance on JPEG / TIFF images, they will be adjustments relative to this color temperature = 6500K, color deviation = 3.
As this is not the actual color temperature of the light source when the photograph was taken, you may feel there is a contradiction, but what is strange with this processing format is the displayed color temperature may be inaccurate. There are no limitations to adjusting the white balance.
Relative adjustments are adjustments to the three parameters, color temperature, color deviation and shading adjustments that diverge from the default values color temperature = 6500K, color deviation = 3. The numerical value of color temperature itself is an assumed value and has no meaning, so this method cannot be used to designate white balance with absolute values of color temperature.
Usage is the same as that of "Auto" white balance, gray balance tools and skin color designation tools on RAW data.
For the "JPEG/TIFF" image, the default setting of the "Sharpness" sub-control and the "Noise reduction" sub-control has no effect.
You have to relatively adjust "sharpness" or "noise reduction" from the original "JPEG/TIFF" image, because it has already been processed in the camera or by software.
2.4.3. Feature that cannot be Used for JPEG/TIFF You have to relatively adjust "sharpness" or "noise reduction" from the original "JPEG/TIFF" image, because it has already been processed in the camera or by software.
For the "JPEG/TIFF" image, you cannot use "Demosaic sharp", "Resolution plus", and "Noise reduction" parameter.
Use "Noise canceller" and "False color controls" to remove noise.
Use "Noise canceller" and "False color controls" to remove noise.