5. Saving Development Process and Development Results
This will explain development processing of JPEG images, and how to save the results as JPEG image files.
There are two methods, “Develop”, indicating development of one selected image, and “Batch develop”, indicating development of multiple images at the same time.
| Format | For processing | Processing format | Preview display | Other features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Develop | One image | Real time processing / batch processing | Yes | Possible to set details for each image |
| Batch develop | Multiple images | Batch processing | No | Possible to efficiently batch process |
[Processing format]
Real time processing
Development processing is performed immediately and processing waits until it is complete.
Processing status is displayed in a progress bar.Batch processing
Development processing is registered as a job and registered jobs are processed in the background in order.
You can do other work at the same time, such as adjusting development parameters during batch processing.
Batch processing status is displayed in the “Batch development status” sub-control.
In addition, there is a “Composite selected images” function that composite images of multiple selections and saves them as a single DNG or TIFF images file.
5.1. Develop
This is a method for designating a way to save development processing and development results for selected single image.
It processes following set instructions. You can select from two formats, a format for processing in real time and a format for registering jobs and processing in a batch.
You can also register jobs for batch develop from “Develop” dialog, but compared to designating development with the “Batch develop” function, you can make more detailed settings and confirm development results in advance in the preview display.
 When you click the
When you click the  icon on the “Development settings” sub-control or the toolbar, the “Save as” dialog is displayed.
icon on the “Development settings” sub-control or the toolbar, the “Save as” dialog is displayed.
You can specify the filename to save the developed image, and specify settings for saving.
You can switch between “Saved file” and “Settings” pages in the “Develop” dialog.
When the “Saved file” tab is selected, you can designate the file folder, file name and file type for saving the development results.
When the “Settings” tab is selected, you can make settings for develop while looking at the preview display of the development results.
After confirming instructions for saving files and development settings, click on the “Develop” or “Batch develop” button and begin processing.
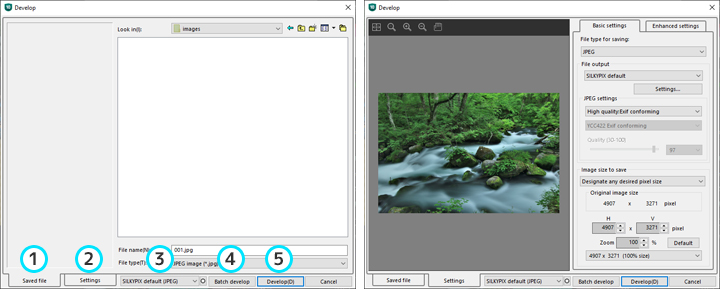
Saved file
This switches to the page for designating details of saved files.
You can designate the file folder, file name and type of file for saving the development results.Settings
Switch to the page for making settings for develop.
You can make settings for develop while looking at the preview display of the development results.Develop tastes
The status of “Develop” tastes will be displayed.
Registered tastes will be displayed when you open the list.
You can switch to develop settings from these tastes.Batch develop
Confirm set development instructions and register development processing to batch development as a job.
Registered jobs are processed as batch development. When job registration is complete, develop is closed, whether or not development processing has been completed and you can go to the next operation.Develop
Confirm set development instructions and begin real time development processing.
The status of processing is displayed on a progress bar until development processing is complete.
5.1.1. Saved File
This page is for designating files to be saved.
Select a location (= folder) for saving files and designate a file name for the file to be saved.
You can only select a JPEG image (*.jpg) as the type of file.
Please make detailed settings related to JPEG images on the “Settings” page.
If there are file names marked for a job registered for batch development in a location (= folder) for saving files, those file names are displayed as marked file names.
When a file name marked here is designated, jobs registered for batch development are cancelled, and if that file already exists, it will be overwritten.
5.1.2. Settings
This page is for making settings for develop while looking at the preview display of saved results.
Settings here include many that have an influence on the developed image itself and on the quality of the image.
Confirm appropriate development instructions while checking the effects and influence on the preview display.
5.1.2.1. Develop Taste
You can select tastes prepared in advance from “Develop” tastes.
It is advisable to register settings you often use as tastes.
5.1.2.2. Basic settings
Image size to save
Set the pixel size of the image to be saved.
There are two ways to make designations, as follows.a) Designate any desired pixel size
When executing develop, you can specify the image size to save. In other words, you can save an enlarged or reduced image with this feature.
You can select an image size from the history, which includes the original image size (100%), the previous size, and the size that has been used for this image and also for other images.
It is convenient to select it from the history if you want to save it with the same size as the previous image.
However, the list shows only the size which is matched to the aspect ratio of the target image.
Click the initialize button to return to default values.b) Fit to designated size
This is the same as the method for “Batch develop”.
Please see “5.3.1.3. Image size to save”.
File output settings
This is the same as the method for “Batch develop”.
Please see “5.3.1.2. File output settings”.
5.1.2.3. Enhanced settings
This is the same as the method for “Batch develop”.
Please see “5.3.2. Enhanced settings”.
5.1.2.4. Preview
Before saving an image, you can check it with the preview, which reflects the effect of the “unsharp mask” and “JPGE compression”.
When you adjust the setting value for the “unsharp mask” or the JPEG image, the preview is automatically refreshed.
It takes a time to complete the development of the entire preview image.
But when part of the image is displayed, only the part is developed, shortening the time for development.
You can change a tool mode or a display magnification from the context menu, which is displayed by right-clicking on the preview image.
5.2. Batch develop
 “Batch develop” is a function that develops multiple images together.
“Batch develop” is a function that develops multiple images together.
A single process of developing and saving to a file a single image is called a “Job.”
When this job is registered in batch develop, batch development processes the registered jobs in the background.
“Batch develop” develops in the background, so if jobs are registered, you do not have to wait for the processing to be completed, but rather you can immediately go to the next operation.
If multiple images are being processed, “Jobs” for the number of images are prepared and these jobs are registered to batch development. They are processed in order.
The following four methods are for performing batch develop.
Batch develop selected images
This is a method for registering a currently selected image or multiple images to jobs in batch development.
A dialog for making settings will be displayed.
Select [Development (D)]-[Batch develop selected images] from the menu, or click on the icon in the toolbar to begin processing.
The toolbar icons change based on the status of selected images.
The (Batch develop selected images) will be displayed only when multiple images are selected.
(Batch develop selected images) will be displayed only when multiple images are selected.Batch develop marked images
This is a method of registering images set with marks for development reservation to jobs in batch development.
A dialog for making settings will be displayed.
Select [Development (D)]-[Batch develop marked images (B)] from the menu, or click on the icon in the toolbar to begin processing.
The toolbar icons change based on the status of selected images.
The (Batch develop marked images) will be displayed only when one image is selected.
(Batch develop marked images) will be displayed only when one image is selected.Immediately batch develop selected images
This is a method for registering a currently selected image or multiple images to jobs in batch development.
No dialog for making settings will be displayed. Current batch development settings will be used.
Select [Development (D)]-[Immediately batch develop selected images] from the menu.
This function is also assigned to the [F5] key by default.Register from “Develop” to Batch develop
This is a method for registering a currently selected image from “Develop” to jobs in batch development.
Job registration is performed from the “Develop” dialog.
Select [Development (D)]-[Develop (D)] from the menu, or click on the icon in the toolbar to begin processing.
Jobs are registered to batch development by clicking on the “Batch develop” button in the “Develop” dialog.
When job registration is complete, the batch development processing dialog will close, even if development processing has not been completed.
Registered jobs are processed in the background.
You can confirm the status of job processing at “Batch development status”.
The number of remaining jobs is also displayed on the batch development status icon on the right side of the toolbar.
5.2.1. Batch Develop Tastes
“Batch Development Settings” can be chosen from tastes prepared in advance.
It is advantageous to register settings used often as tastes.
5.2.2. Basic settings
You can designate the type of file to be saved (only JPEG), pixel size of the image to be saved and development result save settings here.
“Development result save settings” and “Develop” have common setting methods.
Please see “5.3.1.2. File output settings”.
Image size to save
You can specify the size in pixels of each developed image when you want to save an enlarged image or reduced image.
The following three methods are for designating.a) Same size (100%)
The pixel size of the image to be saved will be the pixel size after cropping.
The image is not enlarged or reduced.
The cropping size is not designated, even if the output size is designated in the Crop tool.b) Resize to cropped size
If the output size is designated in the Crop tool, it is resized to the size designated for cropping.
If cropping is not performed and if the output size is not designated in the Crop tool, a same size (100%) is recorded.c) Fit to designated size
This is the same as the method for “Develop”.
Please see “5.3.1.3. Image size to save”.
File output settings
This is the same as the method for “Develop”.
Please see “5.3.1.2. File output settings”.
5.2.3. Enhanced Settings
This is the same as the method for “Develop”.
Please see “5.3.2. Enhanced settings”.
5.2.4. Other settings
Folder to save
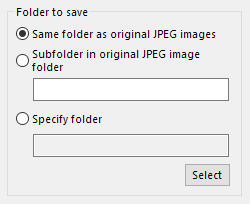 You can select the folder to save a file using the following three ways.
You can select the folder to save a file using the following three ways.Same folder as original JPEG images
You can save a developed image in the same folder as the original JPEG image is stored.Subfolder in original JPEG image folder
You can create a sub-folder under the same folder as the original JPEG image is stored.Specify folder
Click [Select] button to display the “Select folder” dialog, and you can select the folder to save developed images.
When file names are conflicted
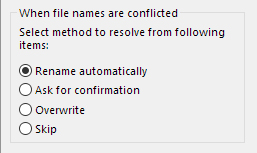 Select an option for when there is a file of the same name as a file output to that destination.
Select an option for when there is a file of the same name as a file output to that destination.
If you select “Overwrite”, the existing file will be overwritten and lost.
Please be extremely careful.
You can select one of the following four types of measures.Rename automatically
A different file name is automatically created and given to the file as RAW data.Ask for confirmation
A dialog box for confirming how to handle the file is displayed.
Please decide the file name.Overwrite
When the file name exists already, SILKYPIX JPEG Photography 10 overwrites the existing file automatically.Skip
When the file name exists already, SILKYPIX JPEG Photography 10 skips saving the file.
The file output in the above process is specified in detail at ‘5.3.1.2. File output settings’.
The default naming conventions use the base name of the JPEG file for image processing.
Don’t remove ‘Develop mark’ after develop
If you leave the check for ‘Don’t erase “Develop mark” after processing’, the “Develop mark” will not be removed.
If a mark for reserving development is being utilized as a mark for job registration, please remove the check.
5.2.5. Batch development status
 In order to check the batch development status, select [View (V)]-[Batch development status] from the menu or click on
In order to check the batch development status, select [View (V)]-[Batch development status] from the menu or click on  in the toolbar to make the “Batch development status” sub-control appear.
in the toolbar to make the “Batch development status” sub-control appear.
Switch and display two kinds of information by selecting tabs in the “Batch development status” sub-control.
5.2.5.1. Waiting
Jobs currently under batch development and a list of jobs waiting to be processed are displayed.
You can delete a selected job with the  icon.
icon.
When you delete a job here, batch development for the deleted job will not be performed.
5.2.5.2. Finished
This will display a list of completed batch development jobs.
You can delete a selected job with the  icon.
icon.
Jobs displayed here have already completed batch development processing, so deleting a job is only erases it from the displayed list so that it will not be seen.
Jobs displayed here will accumulate and increase as batch development proceeds.
Delete and arrange jobs when the number of jobs increases and the list becomes difficult to understand.
A context menu will appear when you select a job and right click on it.
By selecting “Open with Explorer (O)” after you select a job, you can open the developed and saved JPEG image file in Explorer.
You can also delete a selected job from the context menu.
5.2.5.3. Pausing and restarting batch development
Batch development processing can be paused.
All batch development will be halted by clicking on  on the bottom right.
on the bottom right.
Click on  when paused to restart batch development.
when paused to restart batch development.
5.3. Settings for development and saving
Setting items common in both “Develop” and “Batch develop” are explained here.
5.3.1. Basic Settings
Basic settings differ slightly between “Develop” and “Batch develop”, but items that can be set in the same way will be explained.
5.3.1.1. File type for saving
From the drop down list, you can only select JPEG file. When you want to set this in detail, use the “File output settings” dialog as described below.
5.3.1.2. File output settings
By registering a setting status from “File output settings” that you often use as a taste, you can easily switch settings by selecting that taste.
You can also set JPEG saving formats here.
There are many detailed setting items in “File output settings”.
Click on the “Setting details” button and open the “File output settings” dialog to make settings for all items.
Please see “9.1. File output settings” for details.
You can make detailed settings for “JPEG” here.
Items that can be set here are the same as the items that can be set with “Setting details”. Please see “9.1.2. JPEG settings” for details.
5.3.1.3. Image size to save
You can specify the size in pixels of each developed image when you want to save an enlarged image or reduced image.
The methods for designating pixel size for resizing differ slightly between “Develop” and “Batch develop”.
You can record and save at an appropriate pixel size that meets the purposes of the image.
5.3.1.3.1. Fit to designated size
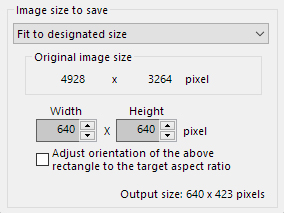 You can designate a size for the image to be saved and make settings so that you save it resized to the pixel size you designated.
You can designate a size for the image to be saved and make settings so that you save it resized to the pixel size you designated.
Select “Fit to designated size” in “Image size to save”.
It will be saved at a pixel size within the restricted size that was designated.
This setting method can be set for both “Develop” and “Batch develop”.
When creating the picture for a slide show that are displayed on a particular display, you can specify a display size. For example, when you want to display images on a VGA display, you can specify the display size of 640x480.
By this setting, the developed image files are saved with the size of 640x480. Therefore, you do not need to adjust the image size at the slide show.
- [Adjust orientation of the above rectangle to the target aspect ratio]
When you check this setting, the specified size is automatically adjusted to match the orientation with the aspect ratio of the target image.
For example, when specifying 640x480 as size, the result size will be inscribed to 640x480 for the lateral image and it will be inscribed to 480x640 for the longitudinal image.
5.3.2. Enhanced settings
Settings for imprint data and unsharp mask are made here.
5.3.2.1. Imprint data
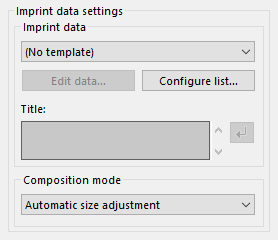 As the name of the function implies, “Imprint data” allows you to imprint the date and time the photograph was taken onto the development results.
As the name of the function implies, “Imprint data” allows you to imprint the date and time the photograph was taken onto the development results.
In addition to the date and time the photograph was taken, you can also include image information, optional characters and credit images on the development results.
You can imprint the date and time the photograph was taken and image information by selecting prepared data for imprint data.
Creating “Imprint data” is required for imprinting a credit image you prepared
Only JPEG images and TIFF images can be selected as images to be imprinted.
Semitransparent images are also compatible with imprinting because it is compatible with TIFF with transparent color information.
Imprint data
Select which data for imprint data you will use.Edit data
Edits the selected imprint data.
Please refer to “9.7.1. Edit imprint data” for details.Configure list
Make settings for the data for imprint data
Please refer to “9.7. Imprint data settings” for details.Title
Set the title.
Use this if you want to temporarily set characters without changing the data for imprint data. The character string entered here is replaced when the control character “%t” of the character string for the data for imprint data is set. Multiple lines can be set.Composition mode
Make settings for the type of composition for the data for imprint data.
For “Develop”, select an appropriate composition mode while looking at the preview display.Automatic size adjustment
Resize the composite characters and image to match the image size of the output development results.
It is adjusted to maintain the relative size.
Select this setting when imprinting to file output.Composite by the fixed-size
Composite characters and images are composed to the set size.
Use when the size of the characters for imprinting is fixed when printing.
Edit the data for imprint data if the position of the letters and image for printing is not appropriate.
5.3.2.2. Unsharp mask
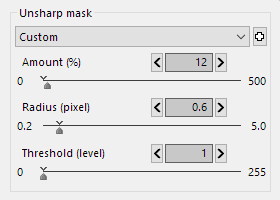 This feature allow you to apply the unsharp mask filter to the developed image
This feature allow you to apply the unsharp mask filter to the developed image
Unsharp mask is applied to results after development and resizing. You can adjust in terms of Amount (%), Radius (pixel) and Threshold (level).
In addition to the sharpness set as a development parameter, use this when you want to add more sharpness in accordance with your purpose and output format for the development results.
Please use this feature according to your purpose and the output type, apart from the sharpness specified by the development parameter.
The “sharpening” specified by the development parameter should be used for each image to adjust resolution.
The other hand, the “unsharp mask filter” should be used for a certain purpose and the output type. For example, when you want to reduce an image for using on a website, you can use the unsharp mask to make up for the sharpness of the image, which will be lost by the image reduction. Or when you want to prepare an image for printing, you can use the unsharp mask to increase image sharpness, avoiding blurred prints.
Please refer to ‘10.1.5. Proper Use of Sharp in Development Parameters and Unsharp Mask when Developing / Printing’ for more details.
5.3.2.2.1. Amount
You can specify the “amount” when you use the “unsharp mask”. The larger the value is, the stronger the sharpness is.
5.3.2.2.2. Radius
Radius sets the width of edge of the object to be emphasized.
The larger the value is, the wider the edge is (stronger sharpness), and the smaller the value is, the narrower the edge is (weaker sharpness).
Typically, setting the range between 0.5-1.0 is recommended.
5.3.2.2.3. Threshold
If the value is set smaller, sharpness is emphasized regardless of the clearness of the edges of objects.
If the value is set larger, sharpness is emphasized only where the edges of objects are clearer to some degree.
You can prevent noise in an image with this parameter, typically, when it is set to ‘1’. Please adjust this parameter to balance noise and sharpness.
5.4. Composite selected images
“Composite selected images” is a function to composite selected images and save them as JPEG-format files.
“Composite selected images” dialog appears by clicking the ![]() icon on the toolbar or by right-clicking the selected image on the thumbnail and selecting “Composite selected images” from the context menu that appears.
icon on the toolbar or by right-clicking the selected image on the thumbnail and selecting “Composite selected images” from the context menu that appears.
* This function is available only when multiple images are selected.
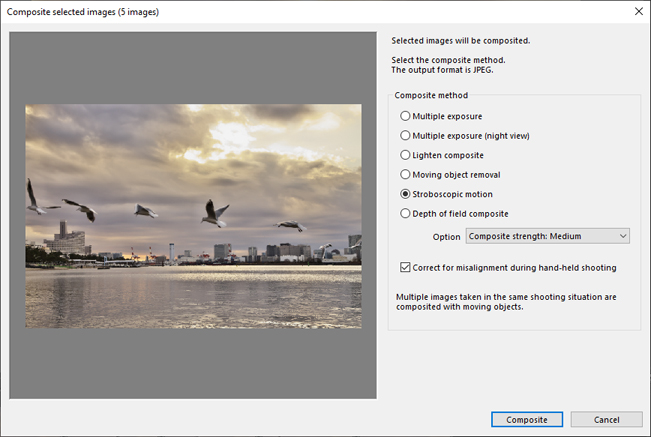
By selecting Composite method and clicking [Composite], you can composite the selected images.
As a condition for compositing, the pixel sizes of the output area of the selected image must all be the same.
If the cropping area is set, it is determined by the size of the pixels after cropping.
5.4.1. Composite method
Select Composite method as desired from the following modes:
Multiple exposure
Composited images are handled equally and result in an image similar to a multiple exposure shot taken with a camera.
If you composite two or more shots of the same scene, you can achieve much more sophistication and high dynamic range photography than normal Noise reduction.Multiple exposure (night view)
Images are composited with a focus on noise reduction, saturation, and black level for night views.
This mode allows you to create a long-exposure, beautiful night scene from multiple photos taken with hand-held shooting.
You can control the synthesis of dark areas with the optional Black level correction.
The stronger Black level correction, the less dark areas are raised or dust appears, but the lighter areas are darkened.- Option
- Black level correction: None
- Black level correction: Weak
- Black level correction: Medium (default)
- Black level correction: Strong
- Black level correction: None
- Option
Lighten composite
Selected images are compared and composited giving priority to the brighter parts of each image.
For example, if you composited an image of fireworks, you can make a photograph of large fireworks.Moving object removal
Multiple images taken in the same shooting situation are composited without moving objects.
For example, if you combine images of intersections where many people are walking, you can create a photograph of intersections where no one is walking.
You can control the removal intensity with Moving object removal options.
The stronger the removal intensity, the easier it is to remove the moving object, but the more unnatural dust is likely to appear.- Option
- Moving object removal: Weak
- Moving object removal: Medium (default)
- Moving object removal: Weak
- Option
Stroboscopic motion
Multiple images taken in the same shooting situation are composited with moving objects.
You can create a sequence photograph that expresses motion by continuously emitting strobes in the dark.
You can control the strength of the composite with “Composite strength” options.
The strongerthe intensity, the more clearly the moving object is composite, but dust will be more likely to appear.- Option
- Composite strength: Weak
- Composite strength: Medium (default)
- Composite strength: Weak
- Option
Depth of field composite
An image that is in focus over a wide area can be created by compositing images with different focus points from near to far.
5.4.1.1. Correct for misalignment during hand-held shooting
When this checkbox is selected, alignment process is performed for images in witch the position of the subject has shifted during hand-held shooting.
This function is based on the representative image and transforms other selected images to match the representative image as much as possible.
Depending on the image, the correction may not be performed successfully.
When correction cannot be performed, “Failed to correct misalignment. Images will be composited without performing alignment.” is displayed below the preview display, and compositing without correction is performed regardless of whether the checkbox is selected.