| SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro | SOFTWARE MANUAL |
| 0. 0.Overview and Introduction | ||||||||
0.1. Section Names
An overview of section names and operation methods of the SILKYPIX® screen display will be explained.
0.1.1. Entire SILKYPIX Display
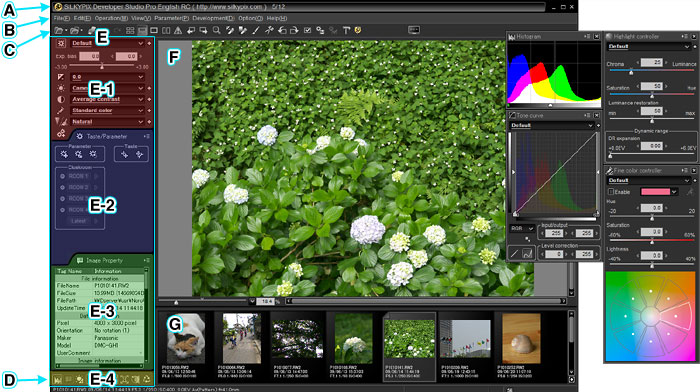
The SILKYPIX® display is composed of the following elements.
0.1.1. Entire SILKYPIX Display

The SILKYPIX® display is composed of the following elements.
| (1) | Main window |
The basic windows in this software are composed of the following parts.
| (E-1) | Main control | |
| The main functions are for selecting tastes prepared for each category of development parameters and for calling up sub-controls for adjusting parameters in detail. Adjust exposure bias here. | ||
| (E-2) | Tab page | |
| Sub-controls for detailed adjustments in each category of the development parameters are displayed here. The sub-controls displayed here can be changed through operations on the Main Control. | ||
| (E-3) | Control box | |
| Sub-controls for detailed adjustments in each category of the development parameters which are regularly used can be displayed in this area. We recommend that you locate sub-controls that you use frequently here. => See "How to Utilize the Control Box." | ||
| (E-4) | Sub-control icon | |
| This switches between displaying and not displaying sub-controls displayed as floating windows. |
| (2) | Floating window |
Sub-controls for adjusting development parameters and windows for displaying status can be displayed as windows independent of the main window.
These are collectively known as floating windows in this software.
These are collectively known as floating windows in this software.
| (3) | Modal dialog |
These are windows that temporarily display various setting dialogs, setting changes, etc.
| (4) | Message box |
Message boxes are displayed while running the software in cases such as special processing, when an error occurs or when you are asked to select the next operation from multiple choices.
Messages displayed here are assigned their own message numbers. Please make note of this message number if there is a problem, such as when an error occurs.
You may be able to use the troubleshooting sections in the manual or on our company's home page.
Messages displayed here are assigned their own message numbers. Please make note of this message number if there is a problem, such as when an error occurs.
You may be able to use the troubleshooting sections in the manual or on our company's home page.
The Menu Bar is an interface from which you can select and execute various operations from the SILKYPIX menu.
Sub-menus for each menu item are displayed in dropdown form when you click on an item from the Menu Bar.
Each item on the Menu Bar is an entry point to locating menu items. They are categorized so that menu items are easy to find.
| * | Here you can assign short-cut keys to any functions you may select. Please refer to "9.4 Key Settings" to learn how to set keys. |
| (1) | File (F) | Menu items related to files are found here. |
| (2) | Edit(E) | Operations of the type that change the status of scenes for processing are found here. |
| (3) | Operation | Items related to preview window operations are found here. |
| (4) | View(V) | Items related to Main Control and Sub-control are found here. |
| (5) | Parameter(P) | Items related to development parameters are found here. |
| (6) | Development(D) | Items related to development processing are found here. |
| (7) | Option(O) | Items related to settings are found here. |
| Delete access history | Delete access history of files and folders for processing. | |
| Initialize location of controls | Initialize sub-control display location and status. | |
| Select Skin | Select SILKYPIX skin. | |
| Display Start Screen | Turn start screen on / off. |
| (8) | Help(H) | Items related to help and SILKYPIX are found here. |
| Initialize user configuration file | Initialize SILKYPIX user configuration files. | |
| Delete temporary file | Delete temporary files prepared for high-speed SILKYPIX processing. | |
| Transmitting error report | Send error report to our company's server. | |
| Test registration | Perform a test to see if it is possible to do an on-line registration of the product key. | |
| Setting for troubleshooting | Adjust settings for troubleshooting. |
| Version information | Display SILKYPIX version information and customer's license information. |

Icons for functions that are frequently used are located in the tool bar.
| * | Many functions that can be selected here can be assigned short-cut keys. Please see "9.4 Key Settings" for how to set keys. |
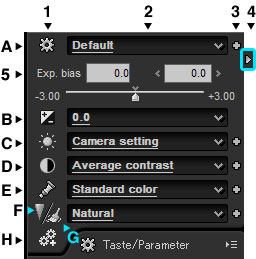 0.1.4. Main Control
0.1.4. Main Control The main control section can be classified into the following five parts.
The main control section can be classified into the following eight operations according to purpose.
The main control section can be classified into the following eight operations according to purpose.
| (A) | Taste parameter | Switch to "taste parameter" sub-control. Tastes selected here are tastes for all categories of development parameters. There are two types of tastes, overall tastes and partial tastes. |
| (B) | Exposure bias | Switch to "Exposure" sub-control. Tastes selected here are partial tastes in the "Exposure" category. |
| (C) | White balance | Switch to "White Balance" sub-control. Tastes selected here are partial tastes in the "White Balance" category. |
| (D) | Tone | Switch to "Tone" sub-control. Tastes selected here are partial tastes in the "Tone" category. |
| (E) | Color | Switch to "Color" sub-control. Tastes selected here are partial tastes in the "Color" category. |
| (F) | Sharpness | Switch to "Sharpness" sub-control. Tastes selected here are partial tastes in the "Sharpness / Noise reduction" category. "Sharpness" and "Noise reduction" exist as separate sub-controls, but they share the same development parameter. |
| (G) | Noise reduction | Switch to "Noise reduction" sub-control. Tastes selected here are partial tastes in the "Sharpness / Noise reduction" category. "Sharpness" and "Noise reduction" exist as separate sub-controls, but they share the same development parameter. |
| (H) | Development | Switch to "Development settings" sub-control. There are no tastes to be selected. |
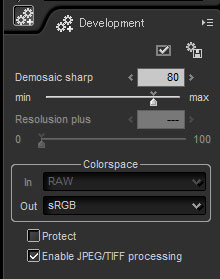 0.1.5. Sub-control
0.1.5. Sub-control Sub-controls are controls for detailed adjustments to development parameters.
Located on the tab page of parameter control or displayed as a floating window, each category of development parameters has separate sub-controls. (*1)
Selection / adjustment to parameters through sub-controls are mainly composed of controls for adjusting numerical values using sliders and edit boxes, dropdown lists and check boxes.
Please see "0.1.7. How to Operate GUI" for operation methods.
0.1.6. Sub-control icon Located on the tab page of parameter control or displayed as a floating window, each category of development parameters has separate sub-controls. (*1)
Selection / adjustment to parameters through sub-controls are mainly composed of controls for adjusting numerical values using sliders and edit boxes, dropdown lists and check boxes.
Please see "0.1.7. How to Operate GUI" for operation methods.
| *1 | As an example, "Sharpness" and "Noise reduction" exist as separate sub-controls, but they share the same development parameter category. |
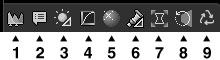
| (1) | Histogram | This is a sub-control that displays a selected scene's histogram. |
| (2) | Image Property | This is a sub-control that displays image properties. You can edit a part of the image information. |
| (3) | White balance adjustment | This is a sub-control for adjusting the white balance according to feeling. |
| (4) | Tone curve | This is a sub-control for minute tone adjustments with the tone curve. It has a level bias function. |
| (5) | Highlight controller | This is a sub-control that adjusts the tint and gradation of parts saturated by color. This is a sub-control that adjusts the tint and gradation of parts saturated by color. |
| (6) | Fine color controller | This is a sub-control for performing hue / chroma / brightness adjustments for each color hue. |
| (7) | Lens aberration controller | This is a sub-control for compensating for shading (when surrounding light quality is low), and distortion, as well as chromatic aberration of magnification. |
| (8) | Rotation/Digital shift | This is a sub-control for rotating images and performing digital shifts that simulate the effects of shifted lenses. |
| (9) | Editing history | This is a sub-control for displaying editing history of development parameters, returning to prior editing conditions and displaying preview windows for comparison with prior editing conditions. |
Various GUI controls are located in parameter controls and sub-controls, but common methods of operation are explained here.
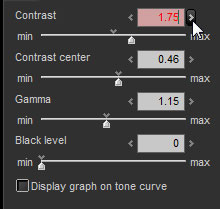

| (1) | Slider control |
This is a SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro standard GUI composed of slider bars, text boxes and buttons for changing numerical values.
Use the following methods to change values.
Use the following methods to change values.
| a) | Drag the needle on the slider to change the value. | |
| b) | Click the slider to change the value. | |
| c) | Click on the arrow located to the left and right of the text box to raise or lower the value. | |
| d) | Directly input numbers in the text box |
Moving the focus to the text box will turn the background of the text box red. This indicates that you have entered direct editing of numerical values mode.
Push the [Enter] key to confirm edited contents and leave the direct editing mode. Moving the focus to other controls will also allow you to confirm edited contents and leave the direct editing mode.
Push the [ESC] key to delete edited contents and leave the direct editing mode.
There are cases in which intermediate value settings cannot be set through other operation methods.
Push the [Enter] key to confirm edited contents and leave the direct editing mode. Moving the focus to other controls will also allow you to confirm edited contents and leave the direct editing mode.
Push the [ESC] key to delete edited contents and leave the direct editing mode.
There are cases in which intermediate value settings cannot be set through other operation methods.
| e) | Raise and lower values with the mouse wheel |
The mouse wheel can be used only when the mouse cursor is within a slider control composed of slider bars, edit boxes and buttons for changing numerical values.
Except for direct editing modes in text boxes, the concept of focus was not adopted for "SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro", so please use the mouse wheel to move the mouse cursor on controls for operations.
Except for direct editing modes in text boxes, the concept of focus was not adopted for "SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro", so please use the mouse wheel to move the mouse cursor on controls for operations.
| f) | Click on the default value mark on the slider bar to set to the default value. |
| g) | Double click on the text box to set to the default value. |

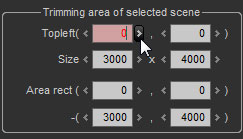
| (2) | Edit control |
This is a SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro standard GUI composed of text boxes and buttons for changing numerical values. It is used to set areas to be trimmed.
| a) | Click on the arrows located to the left and right of the text box to raise or lower the value. | |
| b) | Directly input numbers in the text box |
Moving the focus to the text box will turn the background of the text box red. This indicates that you have entered direct editing of numerical values mode.
Push the [Enter] key to confirm edited contents and leave the direct editing mode. Moving the focus to other controls will also allow you to confirm edited contents and leave the direct editing mode.
Push the [ESC] key to delete edited contents and leave the direct editing mode.
There are cases in which intermediate value settings cannot be set through other operation methods.
Push the [Enter] key to confirm edited contents and leave the direct editing mode. Moving the focus to other controls will also allow you to confirm edited contents and leave the direct editing mode.
Push the [ESC] key to delete edited contents and leave the direct editing mode.
There are cases in which intermediate value settings cannot be set through other operation methods.
| c) | Raise and lower values with the mouse wheel |
The mouse wheel can be used only when the mouse cursor is within an edit control composed of text boxes and buttons for changing numerical values.
Except for direct editing modes in text boxes, the concept of focus was not adopted for "SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro", so please use the mouse wheel to move the mouse cursor on controls for operations.
Except for direct editing modes in text boxes, the concept of focus was not adopted for "SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro", so please use the mouse wheel to move the mouse cursor on controls for operations.
| d) | Double click on the text box to set to the default value. |
This will not function if no default value has been set.
| (3) | Dropdown list |
A dropdown list will open when you click on the "V" mark to the right. Make your selection by moving the mouse and clicking on the selected item.
You can change the selected item with the mouse when the dropdown list is not open.
You can change the selected item with the mouse when the dropdown list is not open.
| (4) | Checkbox |
Turn adjustment items on / off.
0.2. What is SILKYPIX®?
This SILKYPIX ® software generates images by processing RAW data recorded by the digital camera.(*1)
This process of generating an image by processing RAW data is called "development".
RAW data is the unprocessed data recorded as digital light energy information that image sensors capture. Compared to normal JPEG files, RAW files are bigger in size because native information is recorded at the time the photograph was taken.
When photographs are taken in RAW e.g. when photographs are saved as RAW data, you will be able to perform more varied image processing from the unprocessed light energy information even after taking the photograph.
The role of SILKYPIX ® is to get the most out of the photographic merits of RAW and to draw out as much image information as possible when reproducing scenes shot in RAW data. SILKYPIX ® was developed to make this a reality.
*1 ... JPEG/TIFF files can be developed. For more details, please refer to '2.4 How to Handle JPEG/TIFF Image'.
0.2.1. Basic Image Adjustment Items
This process of generating an image by processing RAW data is called "development".
RAW data is the unprocessed data recorded as digital light energy information that image sensors capture. Compared to normal JPEG files, RAW files are bigger in size because native information is recorded at the time the photograph was taken.
When photographs are taken in RAW e.g. when photographs are saved as RAW data, you will be able to perform more varied image processing from the unprocessed light energy information even after taking the photograph.
The role of SILKYPIX ® is to get the most out of the photographic merits of RAW and to draw out as much image information as possible when reproducing scenes shot in RAW data. SILKYPIX ® was developed to make this a reality.
*1 ... JPEG/TIFF files can be developed. For more details, please refer to '2.4 How to Handle JPEG/TIFF Image'.
0.2.1. Basic Image Adjustment Items
In this software, you can adjust various parameters of development procedure. Basic development parameters will be introduced here.
0.2.2. Features of SILKYPIX ® | (1) | Exposure bias | You can adjust parameters at the development process with SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro and obtain the same effect when using the function of the camera. Also, you can use a high-precision "automatic exposure bias" feature, which makes it possible to drive into correct exposure quickly. |
| (2) | White balance adjustment | You can obtain results comparable to photographs taken with appropriate white balance settings on your camera by adjusting parameters when you develop them. You can also obtain results comparable to photographs taken using color temperature conversion filters by adjusting parameters when you develop them. |
| (3) | Sharpness / Noise Reduction Adjustments | You can emphasize the outline of a shot image, or change the noise reduction during the development process. |
| (4) | Tone Adjustment | You can change the tone of the target scene (soft or hard, etc.) during the development process. |
| (5) | Saturation Adjustment | The "color mode" enables you to treat an image like changing reversal film, even after taking a photograph, |
| (6) | Lens aberration controller | You can correct or reduce shading (when surrounding light quality is low), distortion and magnification aberrations from a peculiar lens, and create images of a higher quality. |
| (7) | Rotation/Digital shift | If you find pictures you took with a camera that was tilted, you can adjust the angle by using the "rotation" function after taking a photograph. In addition, the "Digital shift" function has the same effect as using a shift lens which enables you to control the perspective and to shoot a building effectively. |
When you store image data as RAW data and use this software to develop them, you don't have to worry much about adjustments during taking the picture because you can do most corrections at the development process stage. The merits of recording and saving to RAW data compared with saving in JPEG / TIFF are that information is not processed and the amount of information recorded is much richer.
It is also possible to readjust photographs recorded and saved as JPEG / TIFF with this software. However, compared to RAW data, there is less information recorded because JPEG / TIFF images convert to a special color space (sRGB, Adobe RGB, etc.) and color gradation converts to 8bit = 256 steps.
Therefore, if you readjust photographs saved as JPEG / TIFF, the breadth of adjustments are narrowed and deterioration of the image from the adjustments becomes greater.
In order to adjust images while maintaining high image quality, it is necessary to save the RAW data when taking the photograph.
By saving to RAW data and developing with this software, you will be able to obtain very similar results when developing after taking the photograph, as when color and image quality are adjusted at the time the photograph was taken.
SILKYPIX ® greatly shortens the time spent shooting and increases the chance of capturing that important "moment" on the camera.
In addition, with the adoption of a high development algorithm, SILKYPIX ® has the following features.
It is also possible to readjust photographs recorded and saved as JPEG / TIFF with this software. However, compared to RAW data, there is less information recorded because JPEG / TIFF images convert to a special color space (sRGB, Adobe RGB, etc.) and color gradation converts to 8bit = 256 steps.
Therefore, if you readjust photographs saved as JPEG / TIFF, the breadth of adjustments are narrowed and deterioration of the image from the adjustments becomes greater.
In order to adjust images while maintaining high image quality, it is necessary to save the RAW data when taking the photograph.
By saving to RAW data and developing with this software, you will be able to obtain very similar results when developing after taking the photograph, as when color and image quality are adjusted at the time the photograph was taken.
SILKYPIX ® greatly shortens the time spent shooting and increases the chance of capturing that important "moment" on the camera.
In addition, with the adoption of a high development algorithm, SILKYPIX ® has the following features.
| (1) | High resolution, High resolving power |
Although it is generally considered that resolution is decided by the type of lens and the number of pixels of the image sensor, a key factor of actual image resolution is the demosaic process during development procedure.
When you select RAW data to record images and use SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro to develop them, you can obtain higher quality pictures than the JPEG image which the camera records in taking a photograph.
When you select RAW data to record images and use SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro to develop them, you can obtain higher quality pictures than the JPEG image which the camera records in taking a photograph.
| (2) | Advanced color separation |
When photographing with a digital camera, the color boundary in high saturation area is lost and becomes white outline, which is a specific phenomena of digital cameras.
This effect called digital haloing is caused by the white outline through the phenomena that occurs when color resolution is low compared to excessive brightness.
We have therefore created a completely new demosaicing logic and embedded it into the software in order to provide advanced color resolution. This logic allows delicate and advanced color resolution.
This effect called digital haloing is caused by the white outline through the phenomena that occurs when color resolution is low compared to excessive brightness.
We have therefore created a completely new demosaicing logic and embedded it into the software in order to provide advanced color resolution. This logic allows delicate and advanced color resolution.
| (3) | Less false color |
Most of digital cameras now have sensors with a structure called Bayer array.
The R, G, and B sensor elements are allocated in order of Bayer array flatly. Each sensor can only capture one of the R, B or G, so false color appears on the edge of picture or area including delicate pattern.
The software reduces this false colors highly effectively with advanced pixel value forecast logic.
Fundamentally, high resolution, high separation capability, and false color reduction are not realized at the same time logically. High resolution causes increased false color phenomenon, and a trail of false color reduction results in low resolution.
However, the software efficiently enables the realization of these processes simultaneously to create natural pictures and colors
The R, G, and B sensor elements are allocated in order of Bayer array flatly. Each sensor can only capture one of the R, B or G, so false color appears on the edge of picture or area including delicate pattern.
The software reduces this false colors highly effectively with advanced pixel value forecast logic.
Fundamentally, high resolution, high separation capability, and false color reduction are not realized at the same time logically. High resolution causes increased false color phenomenon, and a trail of false color reduction results in low resolution.
However, the software efficiently enables the realization of these processes simultaneously to create natural pictures and colors
| (4) | Color noise reduction at high sensitive photography |
When photographing in high sensitivity mode for night photography or in a dark place, noise of the image sensor generates color noise spots on the image, which is specific to digital cameras
These color noise spots appearing irregularly on the picture are very unpleasant to the eyes, and supposedly many photographers avoid high sensitive photography because of this phenomenon.
The software provides a function for reducing the color noise that surprisingly creates clean pictures for high sensitive photography.
With this software, you can select a wide variety of photographic methods and objects to create a new photograph.
These color noise spots appearing irregularly on the picture are very unpleasant to the eyes, and supposedly many photographers avoid high sensitive photography because of this phenomenon.
The software provides a function for reducing the color noise that surprisingly creates clean pictures for high sensitive photography.
With this software, you can select a wide variety of photographic methods and objects to create a new photograph.
| (5) | Hue control for highlight area |
The software has the function to reduce color reverse or overexposure (bleached-out looking) in the highlight area.
For example, when taking a picture of a person, if you increase a development gain to make a skin color white, color shift phenomenon occurs and highlight boundary area often becomes yellow.
The Highlight controller of the software enables color control in over exposed area and creates fine color adjustment in these highlight areas.
For example, when taking a picture of a person, if you increase a development gain to make a skin color white, color shift phenomenon occurs and highlight boundary area often becomes yellow.
The Highlight controller of the software enables color control in over exposed area and creates fine color adjustment in these highlight areas.
| (6) | Real color reproducibility with high linearity |
In order to create accurate colors with various types of light sources, we have embedded our unique color matching logic based on multiple color matching data acquired in many test pictures.
Many types of light source with various spectral distributions, such as sunlight (natural light), fluorescent light, tungsten filament lamp, glow of sunset, electric flash and combination of them are supported, which realizes accurate color reproducibility.
Based on this color reproduction, you can utilize "3-dimensional color mapping methods, "which converts colors into 3-dimentional data to create (Memory color) expressing similar colors with the colors in a human's memory, (Portrait color), expressing highlights of the skin, and Film taste expressing colors in a positive (Film color)"You can use these color modes according to its utilization or picture image.
Also, '4.10 Fine Color Controller' can change the precise color and to control the delicate color.
Many types of light source with various spectral distributions, such as sunlight (natural light), fluorescent light, tungsten filament lamp, glow of sunset, electric flash and combination of them are supported, which realizes accurate color reproducibility.
Based on this color reproduction, you can utilize "3-dimensional color mapping methods, "which converts colors into 3-dimentional data to create (Memory color) expressing similar colors with the colors in a human's memory, (Portrait color), expressing highlights of the skin, and Film taste expressing colors in a positive (Film color)"You can use these color modes according to its utilization or picture image.
Also, '4.10 Fine Color Controller' can change the precise color and to control the delicate color.
| (7) | Highlight reproduction control by the "dynamic range compression" |
The "dynamic range" control function allows you to make the best use of RAW's ability, which has enough "dynamic range" and records whiter energy than the white point.
You can obtain the smooth gradation in highlight area similar to film.
You can obtain the smooth gradation in highlight area similar to film.
0.3. Difference to Other Photo Retouching Software
RAW development process with SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro and image processing with a photo retouching software are similar.
While various types of photo retouching software that support RAW data are increasingly available in the market, there is a critical difference between them. Understanding of the difference helps you to use SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro to its fullest.
The important point is that this software always starts every image processing function based on RAW data.
When you change parameters in image processing (for example, changing "Exosure blas", "white balance" or "saturation"), the software always starts processing based on RAW data.
Development parameters are recorded in separate files different from RAW data.
Therefore, although the workload for the computer increases, you can obtain a lot of benefits described below.
While various types of photo retouching software that support RAW data are increasingly available in the market, there is a critical difference between them. Understanding of the difference helps you to use SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro to its fullest.
The important point is that this software always starts every image processing function based on RAW data.
When you change parameters in image processing (for example, changing "Exosure blas", "white balance" or "saturation"), the software always starts processing based on RAW data.
Development parameters are recorded in separate files different from RAW data.
Therefore, although the workload for the computer increases, you can obtain a lot of benefits described below.
| (1) | RAW data is not modified (non-degrading image processing). |
Original image data is never changed, so you don't have to worry about losing it even if you make a wrong operation.
The basic design of this software is to "not modify RAW data files."
If JPEG files recorded on a camera are processed with photo retouching software or digital camera editing software, there is a chance that the original image will be overwritten, but with this software the original data file is not modified. (*1)
The basic design of this software is to "not modify RAW data files."
If JPEG files recorded on a camera are processed with photo retouching software or digital camera editing software, there is a chance that the original image will be overwritten, but with this software the original data file is not modified. (*1)
| (2) | You can change parameters until you're completely satisfied |
In photo retouching software, images are processed through independent procedures, proceeding in order, one by one.
For example, if you want to change brightness and then adjust color balance, you have to create the image with a new brightness level and then adjust color balance of the newly created picture image. Adjustment work proceeds while checking each result.
If it is necessary to make minute adjustments to brightness after adjusting the color balance, then you have to choose to either start over again from the beginning or make the image at that time even brighter. Using the first method will not degrade the quality of the image, but it is that much more trouble. The second method is accompanied by image degradation.
Always having to start over again is not actually realistic, and in most cases a certain degree of image degradation is allowed and work proceeds. The user's technique is shown in how he or she lessens degradation in image quality and adjusts the image to fit the purpose.
With this software, image processing always takes place in the optimal order after reading the RAW data. If development parameters are determined, development results will be the same and there will be no degradation to image quality, whatever sequence is employed until adjustments are concluded.
Whether you adjust the white balance after adjusting exposure or adjusting exposure after adjusting the white balance, if the final parameters are the same, the results will be the same.
Therefore, you can change the parameters a number of times until you are satisfied with the result.
For example, if you want to change brightness and then adjust color balance, you have to create the image with a new brightness level and then adjust color balance of the newly created picture image. Adjustment work proceeds while checking each result.
If it is necessary to make minute adjustments to brightness after adjusting the color balance, then you have to choose to either start over again from the beginning or make the image at that time even brighter. Using the first method will not degrade the quality of the image, but it is that much more trouble. The second method is accompanied by image degradation.
Always having to start over again is not actually realistic, and in most cases a certain degree of image degradation is allowed and work proceeds. The user's technique is shown in how he or she lessens degradation in image quality and adjusts the image to fit the purpose.
With this software, image processing always takes place in the optimal order after reading the RAW data. If development parameters are determined, development results will be the same and there will be no degradation to image quality, whatever sequence is employed until adjustments are concluded.
Whether you adjust the white balance after adjusting exposure or adjusting exposure after adjusting the white balance, if the final parameters are the same, the results will be the same.
Therefore, you can change the parameters a number of times until you are satisfied with the result.
| (3) | There is no degradation in image quality from adjustment procedures. |
If you make adjustments through photo retouching software, the adjustment procedures will have an influence on image quality.
You have to decide which one should be adjusted first, brightness or color balance. You also have to consider when you should adjust: Sharpness, Tone curve, and Colorspace for working or the Lens aberration controller.
Always performing these in the optimal procedure demands a high degree of knowledge which to the lay person may result in excessive image quality deterioration.
In addition, even if procedures are appropriate, there are times when gradation or a part of the color gamut is lost due to the combination of procedures.
This software is designed so that image degradation like that through other photo retouching software will not occur, through internal processing that appropriately combines high-grade pipeline image processing that can transmit pixels brighter than pure white.
Leave the image processing order up to SILKYPIX ®. Whatever order the adjustments made to development parameter are performed, SILKYPIX ® will output development results of the highest quality through optimal image processing.
You have to decide which one should be adjusted first, brightness or color balance. You also have to consider when you should adjust: Sharpness, Tone curve, and Colorspace for working or the Lens aberration controller.
Always performing these in the optimal procedure demands a high degree of knowledge which to the lay person may result in excessive image quality deterioration.
In addition, even if procedures are appropriate, there are times when gradation or a part of the color gamut is lost due to the combination of procedures.
This software is designed so that image degradation like that through other photo retouching software will not occur, through internal processing that appropriately combines high-grade pipeline image processing that can transmit pixels brighter than pure white.
Leave the image processing order up to SILKYPIX ®. Whatever order the adjustments made to development parameter are performed, SILKYPIX ® will output development results of the highest quality through optimal image processing.
| (4) | You can restart adjustments whenever you want |
Development parameters are automatically read and updated for each scene, and are managed in a file separate from the RAW data. (*2)Therefore, you can later readjust development parameters from the previous adjustment results.
Development parameters are also concealed in JPEG / TIFF images that saved developments. The development parameters buried in these developments can be viewed with this software and applied to other images for processing. (*3) (*4)
If you have the developed JPEG / TIFF images and the original RAW data, the development parameters for the development results can be read and minute adjustments can be made from the previous adjustment results at any time.
Development parameters are also concealed in JPEG / TIFF images that saved developments. The development parameters buried in these developments can be viewed with this software and applied to other images for processing. (*3) (*4)
If you have the developed JPEG / TIFF images and the original RAW data, the development parameters for the development results can be read and minute adjustments can be made from the previous adjustment results at any time.
| (5) | Perform efficient image adjustments. |
After image processing based on parameters that were set is complete, photo retouching software performs the next image processing, so image processing is complete at the stage when all adjustments have been completed. With this method, in order to go through multiple image processes, you must wait until the previous process is complete, which means that there is a lot of wait time until image processing is complete.
With this software, development processing is gathered for later and can be processed as a batch. You can use a workflow in which development parameters are set while looking at a preview image and development processing is performed later in a batch.
In order to efficiently adjust images, a preview image makes full use of simple image processing and partial development processing, and it is displayed quickly. Even if one image processing has not completely finished, there are many times when making the next adjustment to development parameters is possible, so less time is wasted waiting for the next development parameter to take effect.
Even if a certain amount of time is necessary for actual development processing under the final development parameters, the work can be performed efficiently until the development parameters take effect.
This workflow shows its power when processing large quantities of pictures at the same time.
With this software, development processing is gathered for later and can be processed as a batch. You can use a workflow in which development parameters are set while looking at a preview image and development processing is performed later in a batch.
In order to efficiently adjust images, a preview image makes full use of simple image processing and partial development processing, and it is displayed quickly. Even if one image processing has not completely finished, there are many times when making the next adjustment to development parameters is possible, so less time is wasted waiting for the next development parameter to take effect.
Even if a certain amount of time is necessary for actual development processing under the final development parameters, the work can be performed efficiently until the development parameters take effect.
This workflow shows its power when processing large quantities of pictures at the same time.
| *1 | It is possible to rewrite rotation information tags, depending on the settings, on JPEG / TIFF / DNG images. |
| *2 | Development parameters are automatically recorded in a "SILKYPIX_DS" sub-folder created within folders that contain RAW data for editing and JPEG / TIFF / DMG images. |
| *3 | Development parameters are buried within the Exif information in JPEG / TIFF images that record development results. They will not be buried if not recorded with Exif information. |
| *4 | Spotting tool information is not included in development parameters buried in JPEG / TIFF images that record development results. |
| * | From an early stage, our company developed this kind of "non-degrading image processing" (named OIP technology by our company) and adopted it for many products beginning with digital camera software called "Daisy Digital Camera Friend" which was sold in 1999. With SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro, we have applied the technology to such processes that irregular images like Distortion Correction and, Digital Shift and implemented a completely continuous image processing in those processes. The process causing rotation and deformation of image must be usually executed after development, however, this software allows users to skip this step and enables a complete set of smart workflow from the basic adjustment, such as exposure and white balance, to lens aberration correction. |
0.4. Differences with conventional products
Functions that have been added / modified to "SILKYPIX® Developer Studio Pro" will be explained here.
0.4.1. Development processing / Output processing
0.4.2. Displays
0.4.3. Operations / GUI
0.4.4. Other
0.4.1. Development processing / Output processing
| (1) | Automatic dodging function |
This is the dodging / burning function also included in SILKYPIX ® Marine Photography.
It automatically judges the photograph, adjusts the exposure in each area and createsa good-looking photograph.
It automatically judges the photograph, adjusts the exposure in each area and createsa good-looking photograph.
| (2) | Spotting tools |
This is a function that modifies the image, such as removing dust found on the image sensor and deleting scratches in the image.
| (3) | Supports JPEG / TIFF input color space |
The ICC profile recorded in JPEG / TIFF image files can be set as an input color space.
| (4) | Support to output color space other than sRGB / Adobe RGB |
An ICC profile can be set as the output color space as desired.
| (5) | Supports printing color management |
An ICC profile for printing is used, and color management for printing can be performed.
| (6) | Function for imprinting the date |
The date and time the photo was taken, registered credit images, etc. can be imprinted on the image when development results are output to file or printed.
| (7) | Image properties editing function |
Image property information recorded as Exif information on development results can be edited. This is also available for IPTC standard information.
| (8) | Batch development processing |
The function for processing "Batch development" used up to now has been improved, and a batch development function that processes in the background has been achieved.
| (9) | High speed development processing |
Development processing has accelerated compared to earlier versions by efficiently using multi-processors and making full use of many cache mechanisms.
| (1) | Multi preview display |
Divide the preview into two and compare to another scene or to images reflecting different development parameters.
| (2) | Improved combination display |
Combination display variations have increased to handle a bigger variety of screen layouts.
| (3) | Improved sorting display modes |
Operation methods for selecting displays have improved, such as displaying marked or selected scenes.
| (1) | Improved tone curve / control |
A level correction function was added and improvements were made in displaying the histogram in the background as reference information until just before tone curve processing.
| (2) | Edit history |
A control for managing the edit history of development parameters was added and functions were strengthened much more than the previous undo / redo functions.
In addition, the number of scenes retaining edit history was expanded to 20 scenes and history is no longer lost, even when switching scenes.
Furthermore, it is linked to the multi preview function and the status of edit history can be compared on screen.
In addition, the number of scenes retaining edit history was expanded to 20 scenes and history is no longer lost, even when switching scenes.
Furthermore, it is linked to the multi preview function and the status of edit history can be compared on screen.
| (3) | Function for pasting from latest editing parameter |
The latest status of the edited development parameters is automatically recorded in a special room for temporary records.
Work can continue on other successive scenes using the edited status of another scene worked on to that point by pasting the image parameters stored in that room to another scene.
Work can continue on other successive scenes using the edited status of another scene worked on to that point by pasting the image parameters stored in that room to another scene.
| (4) | Bundle taste functions for each setting |
Settings used often can now be registered in tastes.
| (5) | Improved key settings |
The format for assigning functions to short cut keys was improved in order to raise work efficiency by assigning functions used often to short cut keys.
| (1) | Advanced license registration function |
A method is provided for automatically registering licenses, reregistering and transferring licenses to other PCs from PCs connected to the Internet.
| (2) | Export / Import settings |
Functions for exporting settings such as "Development result save settings," "Display settings," "Function settings" and "Key settings" and saving them to a file, as well as for importing and restoring them are included.